
Naming Carboxylic Acids
(Chemical) Definition of Carboxylic Acids:
Carboxylic Acids are organic chemical compounds that include:
- a -carbonyl group (i.e. an oxygen atom attached to a carbon atom by a double covalent bond)
and - a -hydroxyl group (i.e. an oxygen atom attached to a carbon atom by a single covalent bond and a hydrogen attached to the same oxygen atom by another single covalent bond)
... both attached to the same carbon atom.
Due to carbon having a valancy of 4, the carbon atom to which these two functional groups are attached must always be located at the end of a chain of carbon atoms, the length of the chain varying from one (carbon atom) upwards:
Carboxylic Acid molecules can vary in size up to very long molecules most of which consist of carbon atoms attached to each other and also to hydrogen atoms.
Names of Carboxylic Acids in General
Carboxylic Acids are named according to the same system as other organic compounds, with the suffix -oic acid used to indicate that both a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group are both attached to the same carbon atom, which is located at the end of a chain or branch of carbon atoms forming the molecule (except in the case of methanoic acid, which includes only one carbon atom).
The first step to consider when working out the name of a carboxylic acid molecule is the number of carbon atoms forming a chain. If they are attached together in a linear (i.e. unbranched) configuration then the number of carbon atoms is indicated according to the same system as used for naming alkanes.
However, if the carbon atoms do not form a simple linear chain, but include branches, the longest linear chain of carbon atoms within the molecule determines the base of the name of the compound, onto which is added information about the branches incl. their lengths in terms of the number of carbon atoms in each branch (i.e. methyl- usually indicates a branch consisting of just one carbon atom attached to the main chain, ethyl- indicates a branch of two carbon atoms in length, etc.) and their positions along the longest linear carbon chain (e.g. attached to the 2nd carbon, 3rd carbon, etc.).
The simplest linear carboxylic acids are named and their structures shown in the following table.
Names and Structures of simple Linear Carboxylic Acids
The first ten members of the homologous series of linear carboxylic acids are represented below. The simple structures drawn below show bond types such as single and double bonds, but not accurate bond angles.
Name and simple formula |
Simple Structure showing bond types but not accurate bond angles |
Examples of other names (synonyns) |
|
1 |
methanoic acid (CH2O2) |
||
2 |
ethanoic acid (C2H4O2) |
 |
|
3 |
propanoic acid (C3H6O2) |
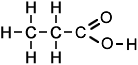 |
|
4 |
butanoic acid (C4H8O2) |
 |
|
5 |
pentanoic acid (C5H10O2) |
 |
|
6 |
hexanoic acid (C6H12O2) |
 |
|
7 |
heptanoic acid (C7H14O2) |
 |
|
8 |
octanoic acid (C8H16O2) |
 |
|
9 |
nonanoic acid (C9H18O2) |
 |
|
10 |
decanoic acid (C10H20O2) |
 |
|
- Methanoic acid (CH2O2)
Simple Formula:HCOOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- methanoic acid
- formylic acid
- aminic acid
- hydrogen carboxylic acid
- formira
 and others.
and others.
- Ethanoic acid (C2H4O2)
Simple Formula:CH3COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- acetic acid
- ethylic acid
- vinegar acid
- methanecarboxylic acid
 and others.
and others.
- Propanoic acid (C3H6O2)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- propionic acid
- ethylformic acid
- metacetonic acid
- methylacetic acid
- pseudoacetic acid
- methyl acetic acid
- ethanecarboxylic acid
- carboxyethane
 and others.
and others.
- Butanoic acid (C4H8O2)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- n-butanoic acid
- butyric acid
- n-butyric acid
- 1-butyric acid
- butanic acid
- propylformic acid
- butanic acid
- ethylacetic acid
- 1-propanecarboxylic acid
- butoic acid
 and others.
and others.
- Pentanoic acid (C5H10O2)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- n-pentanoic acid
- valeric acid
- n-valeric acid
- valerianic acid
- 1-butanecarboxylic acid
- propylacetic acid
- butanecarboxylic acid
- pentoic acid
 and others.
and others.
- Hexanoic acid (C6H12O2)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- n-hexanoic acid
- caproic acid
- n-caproic acid
- capronic acid
- hexoic acid
- butylacetic acid
- pentiformic acid
- n-hexylic acid
- n-hexoic acid
- pentylformic acid
- 1-pentanecarboxylic acid
 and others.
and others.
- Heptanoic acid (C7H14O2)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- n-heptanoic acid
- enanthic acid
- oenanthic acid
- enanthylic acid
- n-heptylic acid
- n-heptoic acid
- heptoic acid
- heptylic acid
- 1-hexanecarboxylic acid
- hexacid C-7
 and others.
and others.
- Octanoic acid (C8H16O2)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- n-octanoic acid
- caprylic acid
- n-caprylic acid
- octylic acid
- n-octylic acid
- octoic acid
- n-octoic acid
- 1-heptanecarboxylic acid
- enantic acid
- octic acid
- hexacid C-8
 and others.
and others.
- Nonanoic acid (C9H18O2)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- n-nonanoic acid
- pelargonic acid
- nonylic acid
- pelargic acid
- nonoic acid
- n-nonylic acid
- n-nonoic acid
- 1-octanecarboxylic acid
- hexacid C-9
 and others.
and others.
- Decanoic acid (C10H20O2)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- n-decanoic acid
- capric acid
- n-capric acid
- decylic acid
- caprinic acid
- decoic acid
- n-decylic acid
- n-decoic acid
- caprynic acid
- 1-nonanecarboxylic acid
- C10 fatty acid
 and others.
and others.









