
Naming Alkynes
Definition of Alkynes:
Alkynes are organic chemical compounds that include a triple covalent bond between two carbon atoms. ![]()
That is, alkynes are the class (or category) of organic hydrocarbon compounds that include a part consisting of two carbon atoms attached to each other by a triple covalent bond, which is usually represented in molecular diagrams as three parallel straight lines between the carbon atoms attached together by that triple bond.
Alkyne molecules can vary in size up to very long molecules most of which consist of carbon atoms attached to each other and also to hydrogen atoms.
Names of Alkynes in General
Alkynes are named according to the same system as other organic compounds, with the suffix -yne used to designate the presence in the molecule of a triple carbon-carbon bond.
The first step is to consider the number of carbon atoms forming a chain. If they are attached together in a linear (i.e. unbranched) configuration then the number of carbon atoms is indicated according to the same system as used for naming alkanes. See the examples listed in the table below.
However, if the carbon atoms do not form a linear chain but include branches, the longest linear chain of carbon atoms within the molecule determines the base of the name of the compound, onto which is added information about the branches incl. their lengths in terms of the number of carbon atoms in each branch (i.e. methyl- indicates a branch consisting of just one carbon atom attached to the main chain, ethyl- indicates a branch of two carbon atoms in length, etc.) and their positions along the longest linear carbon chain (e.g. attached to the 2nd carbon, 3rd carbon, etc.).
The simplest linear alkynes are named and their structures shown in the following table.
Names and Structures of simple Linear Alkynes
The homologous series of linear alkynes with the triple bond attached to the first (= last) carbon atom is shown below.
Name and simple formula |
Simple Structure showing bond types but not accurate bond angles |
Previous / Other Names |
|
2 |
ethyne (C2H2) |
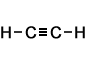 |
|
3 |
propyne (C3H4) |
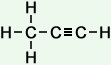 |
|
4 |
butyne (C4H6) |
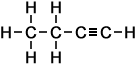 |
|
5 |
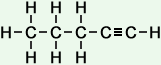
pentyne (C5H8) |
 |
|
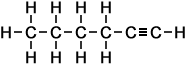
6 |
hexyne (C6H10) |
 |
|
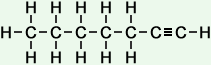
7 |
heptyne (C7H12) |
 |
|
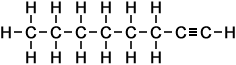
8 |
octyne (C8H14) |
 |
|
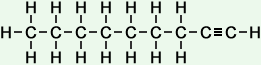
9 |
nonyne (C9H16) |
 |
|
10 |
decyne (C10H18) |
 |
|
- Ethyne (C2H2)
Simple Formula:HCCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- acetylene
- acetylen
- ethenylene
- ethine
- ethin
- vinylene
- Propyne (C3H4)
Simple Formula:CH3CCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- 1-propyne
- prop-1-yne
- methylacetylene
- methyl acetylene
- allylene
- propylene tetramer
- Butyne (C4H6)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- 1-butyne
- but-1-yne
- butyne-1
- ethylacetylene
- ethyl acetylene
- Pentyne (C5H8)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- 1-pentyne
- pent-1-yne
- acetylene
- Hexyne (C6H10)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- 1-hexyne
- hex-1-yne
- butylacetylene
- n-butylacetylene
- Heptyne (C7H12)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- 1-heptyne
- hept-1-yne
- amylacetylene
- Octyne (C8H14)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- 1-octyne
- oct-1-yne
- hexylacetylene
- Nonyne (C9H16)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- 1-nonyne
- non-1-yne
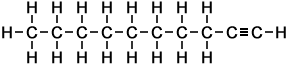
- Decyne (C10H18)
Simple Formula:CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CCHSimple Structure:
 *Examples of other / previous names:
*Examples of other / previous names:- 1-decyne
- octylacetylene
See also the related page about functional groups in organic molecules, which includes the nitrile group among others.









